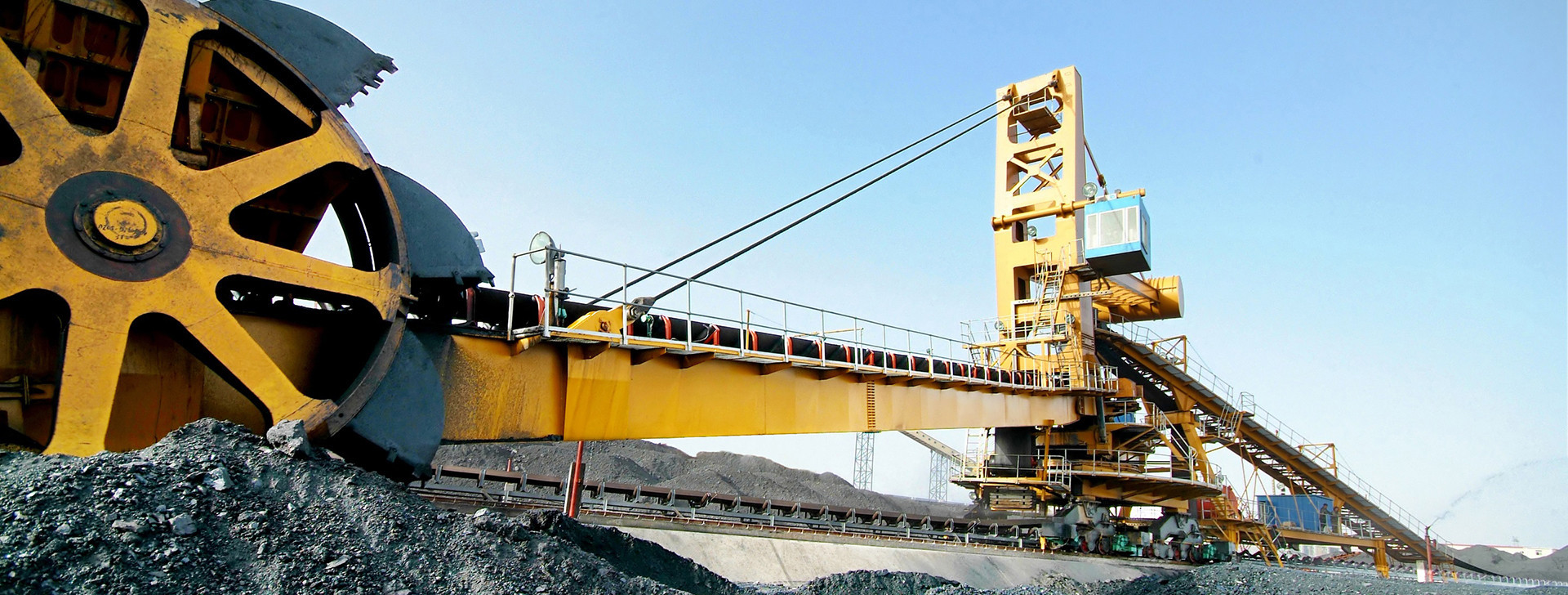
Mining industry
When it comes to protecting industrial mining and processing equipment from abrasive wear, several effective solutions are available, including bimetal technology, cast basalt, and oxide ceramics. Each of these technologies has unique features and advantages:
1. Bimetal involves applying a wear-resistant layer to equipment surfaces using welding methods. This layer typically consists of high-strength alloys or carbides, such as chromium carbide. The overlay provides excellent resistance to abrasion and impact, protecting the underlying equipment from wear. In the mining industry, bimetal is commonly used to protect heavily worn and abraded equipment and components, including:
- Excavator buckets. These large buckets are used to extract and transport large amounts of material and are subject to significant wear and abrasion during operation.
- Dump truck bodies. Dump truck bodies are constantly exposed to abrasive materials such as rock and ore, which can quickly wear down the metal surface.
- Crusher hammers. These parts of crushing equipment are responsible for breaking down the processed material and are subjected to intense wear and abrasion.
- Conveyor belts and rollers. Conveyor belts and rollers undergo constant friction and wear as they transport materials throughout the mining process.
- Mill liners. Mills are used to grind ore and other materials, and the liners protecting the mill's interior are subjected to heavy abrasion.
- Pump impellers and housings. Pumps are used to transport fluids and slurries throughout mining operations, and impellers and housings in contact with the transported materials often wear out quickly.
 |
 |
 |
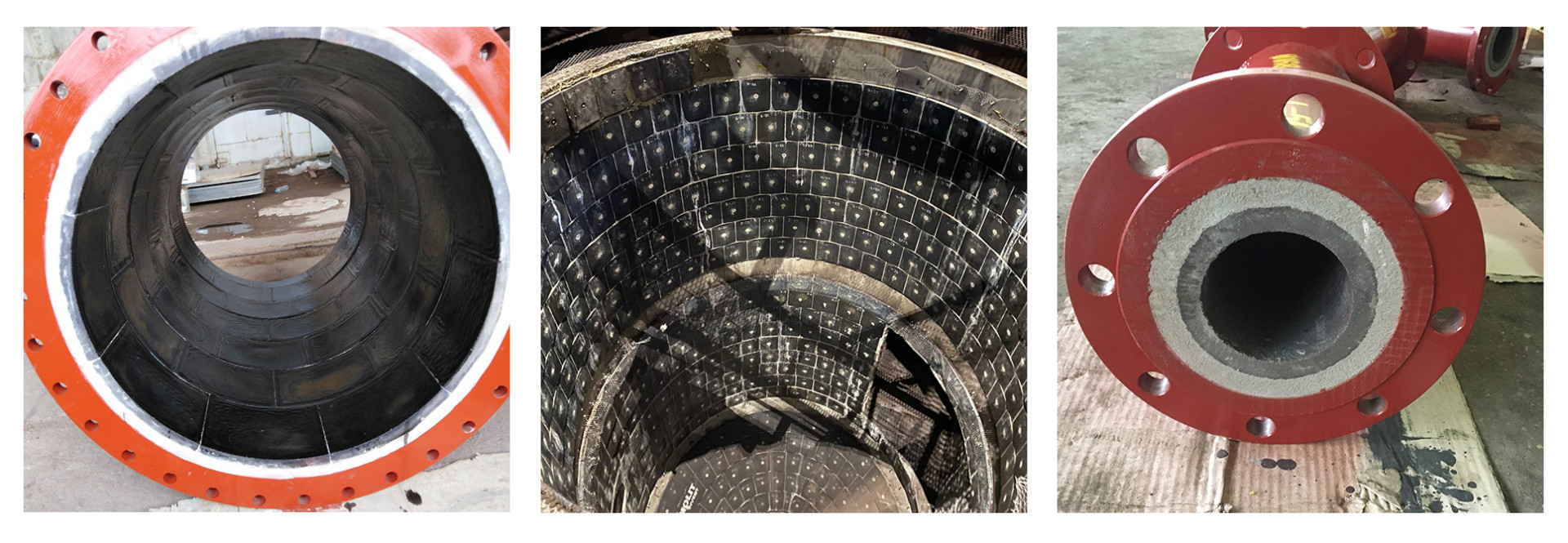
2. Cast basalt is a material made from volcanic rock, featuring exceptional hardness, chemical resistance, and wear resistance. It is created by melting and casting basalt rock into the desired shape, which can then be used as liners, tiles, or pipes to protect equipment. The high hardness, exceptional wear resistance, and ability to withstand high environmental temperatures make cast basalt a valuable material for wear protection in the mining industry. Cast basalt effectively resists abrasive wear, particularly in applications involving high-velocity material flow or high-temperature conditions. Here are a few examples of mining equipment that can be effectively protected using cast basalt lining:
- Chutes and hoppers. Chutes and hoppers are essential components in mining operations for handling and flowing bulk materials. These areas are subject to heavy abrasion and impact. Cast basalt lining can be used to line the internal surfaces of chutes and hoppers, providing superior wear resistance and reducing material degradation.
- Cyclones and separators. Cyclones and separators are used in the mining industry for particle separation, classification, and material recovery. The abrasive nature of the processed materials can lead to wear on the internal surfaces of this equipment. Cast basalt lining can be applied to protect cyclones and separators, extending their lifespan and ensuring the efficiency of separation processes.
- Pipes and bends. Pipeline systems used in the mining industry often experience abrasion and erosion due to the transported materials. Cast basalt lining can be applied to the internal surfaces of pipes, elbows, and bends to minimize wear and extend the lifespan of pipeline systems. It has excellent resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and thermal shock.
- Conveyor components. Conveyors are widely used in the mining industry for handling bulk materials. Components such as conveyor chutes, skirts, and impact zones are subject to wear and impact damage. Cast basalt lining can be applied to these components, reducing wear and minimizing material spillage, thereby increasing conveyor efficiency.
- Vibrating screens. Vibrating screens are commonly used in the mining industry for material classification and separation. Continuous vibration and abrasive contact with particles can lead to wear on the screen surfaces. Cast basalt lining can be applied as a wear-resistant lining for vibrating screen surfaces, extending their lifespan and ensuring the efficiency of screening processes.
- Milling equipment. Mills, such as ball mills and semi-autogenous grinding mills, are crucial equipment in ore processing and grinding operations. Grinding media and ore particles can cause significant wear on the internal surfaces of these mills. Cast basalt lining can be used as a protective lining inside mills, providing superior wear resistance and reducing maintenance requirements.

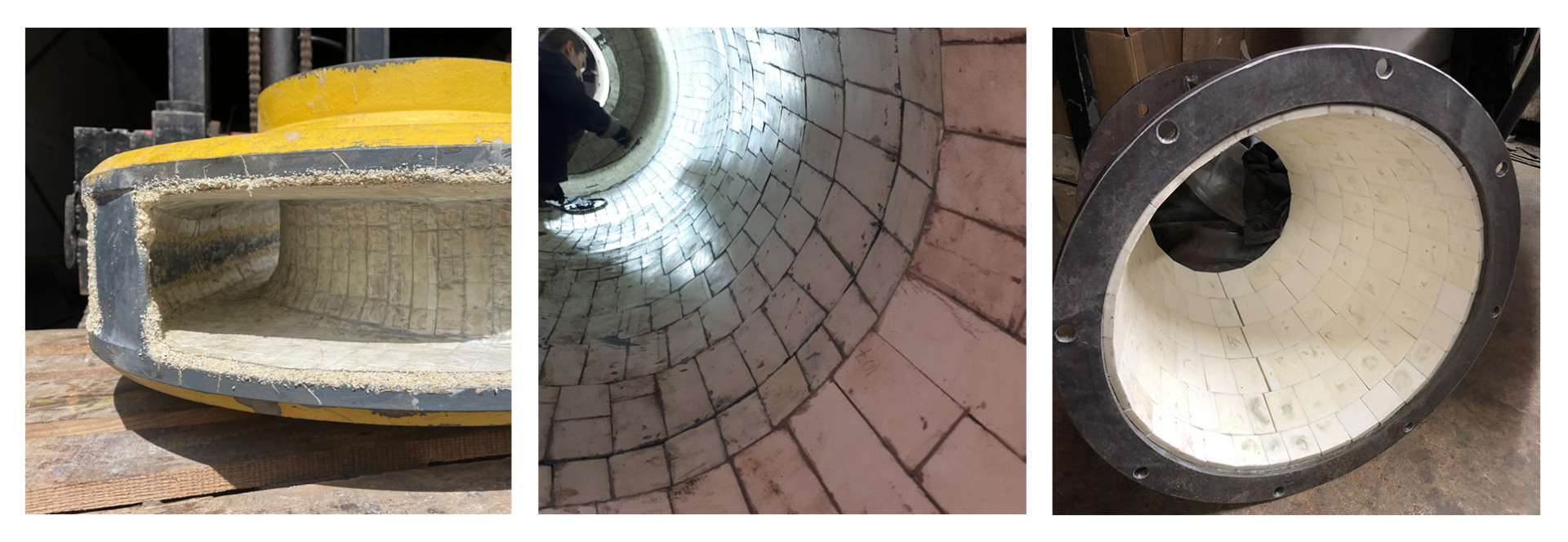
3. Oxide ceramics are engineered ceramic materials with a high content of aluminum oxide, typically exceeding 90%. This material has excellent hardness, strength, and abrasion resistance. Due to these qualities, oxide ceramics are widely used in various areas of the mining industry to protect equipment from wear and abrasion while reducing maintenance needs and enhancing the overall durability of the equipment. Among the most common applications of oxide ceramics in the mining industry are:
- Chutes and hoppers. Chutes are used to transfer material from one conveyor belt to another or from a conveyor belt to a truck or railcar. Chutes are subject to high levels of wear and abrasion from the material flowing through them. High-alumina ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of chutes, protecting them from wear and extending their lifespan.
- Pipes. Pipes are used to transport materials from one place to another in mining operations. Pipes are subject to wear and abrasion from the material flowing through them, especially in areas where the material changes direction or speed. High-alumina ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of pipes, protecting them from wear and extending their lifespan.
- Conveyor belts. Conveyor belts are used to transport material from one place to another in mining activities. Conveyor belts are subject to wear and abrasion from the transported material and friction between the belt and rollers. High-alumina ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of conveyor belts, protecting them from wear and extending their lifespan.
- Hoppers. Hoppers are used to store and feed material into processing equipment. Hoppers are subject to wear and abrasion from the material flowing through them, especially in areas where the material contacts the hopper's surface. High-alumina ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of hoppers, protecting them from wear and extending their lifespan.
- Cyclones. Cyclones are used to separate materials of different sizes and densities. Cyclones are subject to wear and abrasion from the processed material, especially in areas where the material contacts the cyclone's surface. High-alumina ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of cyclones, protecting them from wear and extending their lifespan.

All these materials and technologies have various advantages and may be more suitable for specific applications depending on factors such as operating conditions, material characteristics, and budget considerations. Optimal solutions for protecting equipment from abrasive wear in the mining industry often involve a combination of these materials and technologies, depending on the specific wear challenges and equipment requirements.
It is important to note that the selection and implementation of these solutions should be based on a comprehensive assessment of the equipment, wear patterns, and operating conditions. Working with wear protection specialists or consulting with engineering services can help identify the most suitable materials and technologies for optimal equipment protection in your specific mining and processing operations.
