Coal preparation plants
Reducing equipment wear at a coal preparation plant is a crucial task for the enterprise, and a comprehensive set of measures is directed towards this goal, including the installation of protective coatings on various equipment components.
Lining can be made from various materials, including hard-faced bimetal overlays, oxide ceramics, cast basalt, and more. Protective materials are installed on parts of the equipment that are most susceptible to impact, abrasive, cavitation, chemical, and other types of wear, such as blades, augers, screens, bunker walls, and more.
The advantage of protective coatings is that they can be installed on existing equipment without the need for complete replacement. Additionally, protective coatings can be custom-made for each equipment part, ensuring an optimal balance between coating cost and protective properties.
1. Bimetallic lining is an effective technology for protecting coal preparation plant equipment from wear and abrasion. Examples of equipment and production areas at coal preparation plants where bimetal is commonly used include:
-
Screening equipment. Screening equipment is used to separate coal particles by size. These components are subjected to intense abrasive wear. Bimetal can effectively resist wear on screening equipment, thereby extending its service life.
-
Cyclones. Cyclones are used to separate coal particles from the airflow. These components experience high levels of abrasive wear and can wear out. Bimetal can be used to protect cyclones from wear and extend their service life.
-
Feeders. Feeders are used to transport coal from one production area to another. These components experience high levels of abrasive wear and can wear out. Bimetal can be used to protect feeders from wear and increase their service life.
-
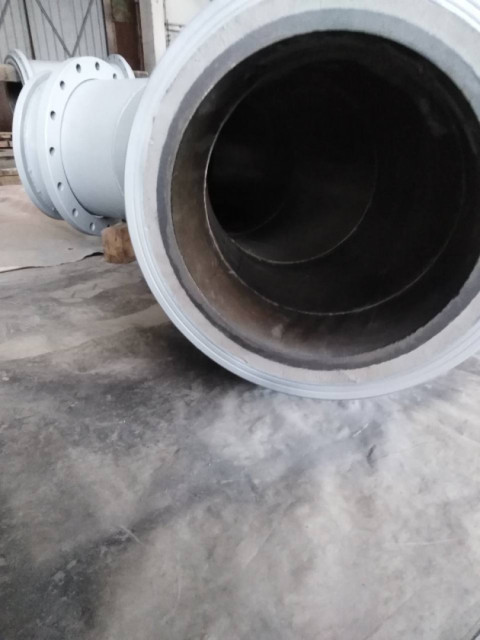
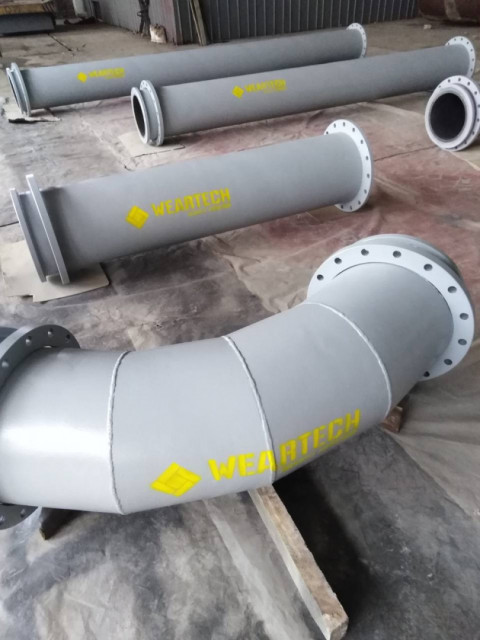
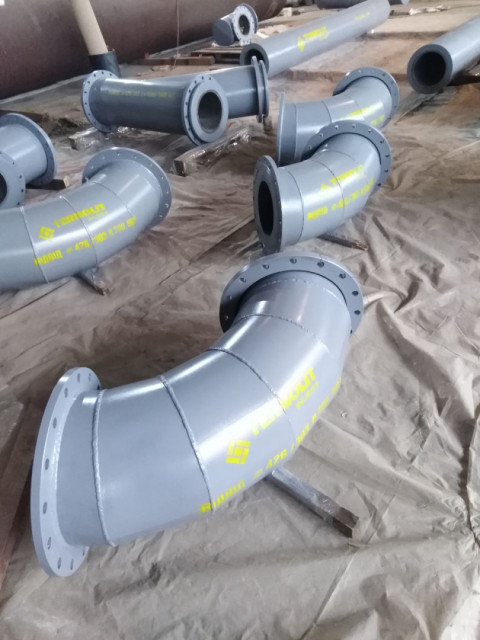
Pipes and chutes. Pipes and chutes are used to transport coal and other materials during the enrichment process. These components experience high levels of abrasive wear and can wear out. Bimetallic lining is used to protect pipes and chutes from wear and increase their service life.
-
Crushers. Individual units and parts of crushers undergo intense abrasive and impact wear during coal particle crushing and require replacement. Bimetal can be effectively used to protect crushers from wear and extend their service life.
 |
 |
 |
2. Cast Basalt. Cast basalt lining can be effectively used to protect technological equipment at coal preparation plants. Among the critically important types of equipment and components at coal preparation plants that are subject to high wear and can benefit from using cast basalt lining are:
-
Chutes and hoppers. Chutes and hoppers are essential components at coal preparation plants where coal undergoes various stages of processing. They are subject to heavy wear due to the abrasive nature of coal and the impact of falling material. Applying cast basalt lining to chutes and hoppers can significantly reduce wear and extend equipment life.
-
Cyclones. Cyclones are typically used to separate coal and ash particles. They are exposed to the abrasive particles of coal and require wear-resistant solutions. Cast basalt lining can be used on the internal surfaces of cyclones to protect against abrasion and increase their durability.
-
Pipelines and chutes. Pipelines and chutes are responsible for transporting coal slurry or water at coal preparation plants. These components are subject to wear and erosion due to the abrasive coal slurry. Applying cast basalt lining to the internal surfaces of pipes and chutes can significantly enhance wear resistance, reducing maintenance and downtime.
-
Screens and vibrating feeders. Screens and vibrating feeders are used to separate and transport coal particles of different sizes. The constant movement and impact of coal can lead to wear on the surfaces of these components. Cast basalt lining can be used to protect screens and vibrating feeders, minimizing wear and extending their service life.
When selecting protective coatings, it is essential to consider the operating conditions of the equipment and the characteristics of the abrasive materials passing through the equipment. For example, ceramic coatings may be more effective when working with low-density particles, whereas hard-faced bimetal lining may be preferable for larger and heavier particles.
3. Oxide ceramics are also widely used for protecting critical technological equipment at coal preparation plants. Here are just a few examples of using oxide ceramics for equipment protection:
- Cyclones. Cyclones are typically used at coal preparation plants to separate coal particles from surrounding air or water. Due to the abrasive nature of coal, cyclones can undergo significant wear. Oxide ceramics can be applied as linings or wear-resistant coatings on the internal surfaces of cyclones to withstand abrasive impacts and extend their service life.
- Dense medium separators. Dense medium separators, also known as heavy media cyclones, are used to separate coal based on its density. These separators often wear out due to the movement of dense media and coal particles. Oxide ceramics can be used to line the internal surfaces of dense medium separators, providing exceptional wear resistance and extending their service life.
- Conveyors and transfer points. Conveyors and transfer points play a crucial role at coal preparation plants, transporting coal at all stages of processing. These components undergo constant abrasion and impact. Oxide ceramics can be used as linings or wear plates in conveyor chutes, transfer points, and other high-wear areas to minimize wear, prevent material leakage, and ensure efficient material flow.
- Screens and sieves. Screens and sieves are used to separate coal particles into different sizes. The constant vibration and abrasive contact with coal can cause significant wear. Oxide ceramics can be applied as wear-resistant linings for screens and sieves, reducing wear and extending their service life, leading to increased screening efficiency.
- Grinding equipment. Grinders, including ball mills and vertical roller mills, are often used at coal preparation plants to reduce the size of coal particles. During the grinding process, these mills experience high levels of abrasive wear. Oxide ceramics can be used as linings or protective coatings inside the mills to enhance wear resistance and minimize maintenance and repair work for this type of equipment.
When using linings, it is also essential to consider the equipment maintenance process and the accessibility of its parts for repair. For example, coatings that need to be replaced too often or are difficult to install may be less effective than coatings with a longer lifespan and easily accessible parts.
Additionally, when selecting a specific type of lining, its impact on the coal processing process should be considered, as some coatings may alter the surface characteristics of the equipment and thus affect the coal processing process.
Overall, considering the operating conditions of the equipment at a specific coal preparation plant, using various types of linings can be one of the most effective methods for reducing wear and increasing equipment productivity.





